Hardora
Hardora Oracle is a decentralized mobile-first hardware oracle for off-chain data computation and data access.
Project Description
The Hardora Oracle is a decentralized, mobile-first, compute-enabled hardware oracle for off-chain data access and computation. The emphasis is on a decentralized, hardware-based, compute-enabled and mobile-first oracle for DApps built on existing blockchains to access off-chain data that is unavailable on-chain.
THE PROBLEM WITH CURRENT ORACLES
Centralization
Most current blockchain oracles are centralized, and those that are decentralized are controlled by a few nodes that contribute to sourcing and validating information. The integrity of the data provided by this oracle network depends on the integrity of these few nodes
Expensive setup
Running a node can be expensive to set up, limiting the number of nodes available; thus, most oracles are centralized or partly decentralized.
Complex Architecture/Consensus
Some current decentralized oracles operate their blockchain network, which has its unique challenges such as scalability and interoperability with existing blockchains. The complex architecture of these oracles and the requirement to set up a node make it difficult for easy integration with an existing blockchain network and scalability for future use of blockchain oracles.
OUR APPROACH
Decentralization
We are democratizing Oracle service for any existing blockchain network, which ensures the integrity of the Oracle network and thus the information provided. This is achieved by allowing nodes to run on mobile computing devices like Android phones and by allowing thousands of people to join the network and become node operators.
Low setup cost and easy setup
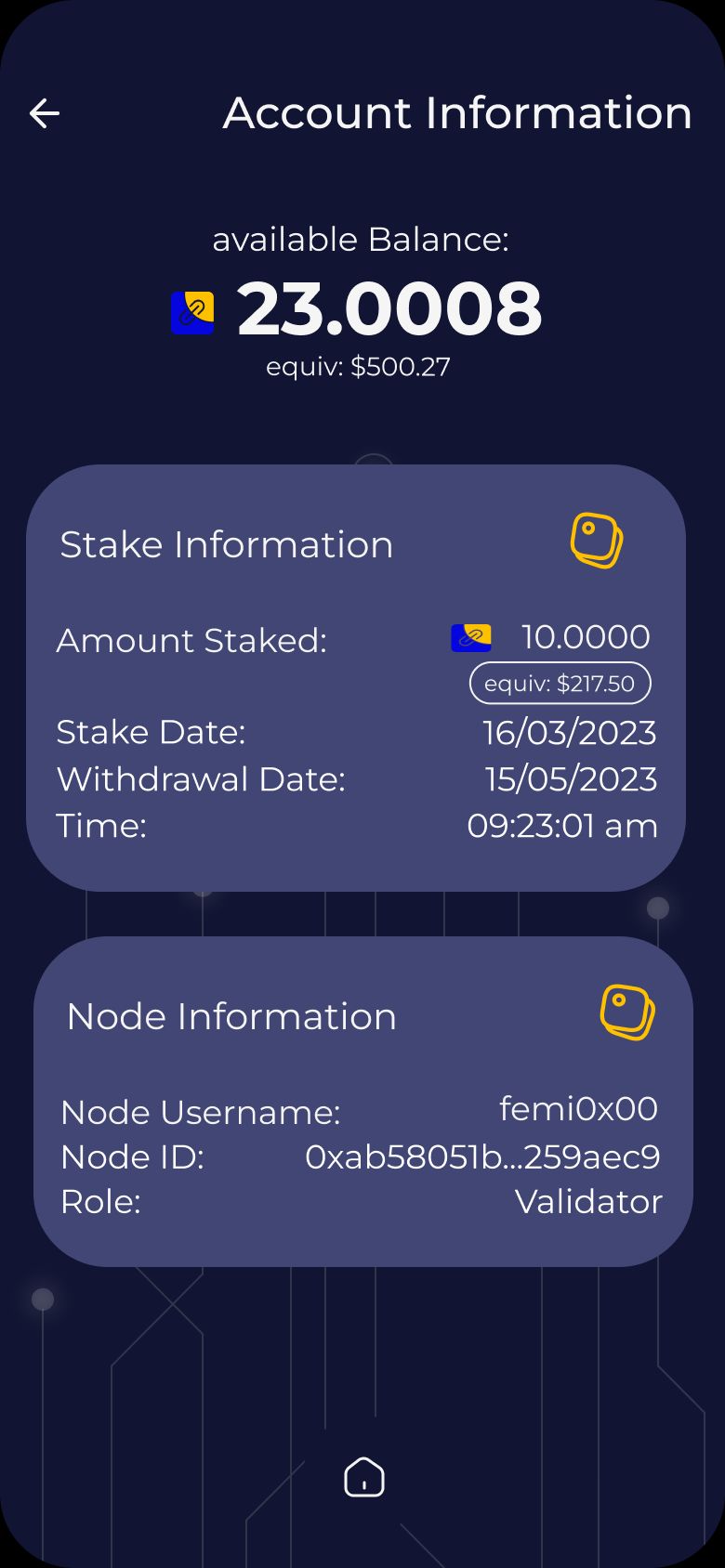
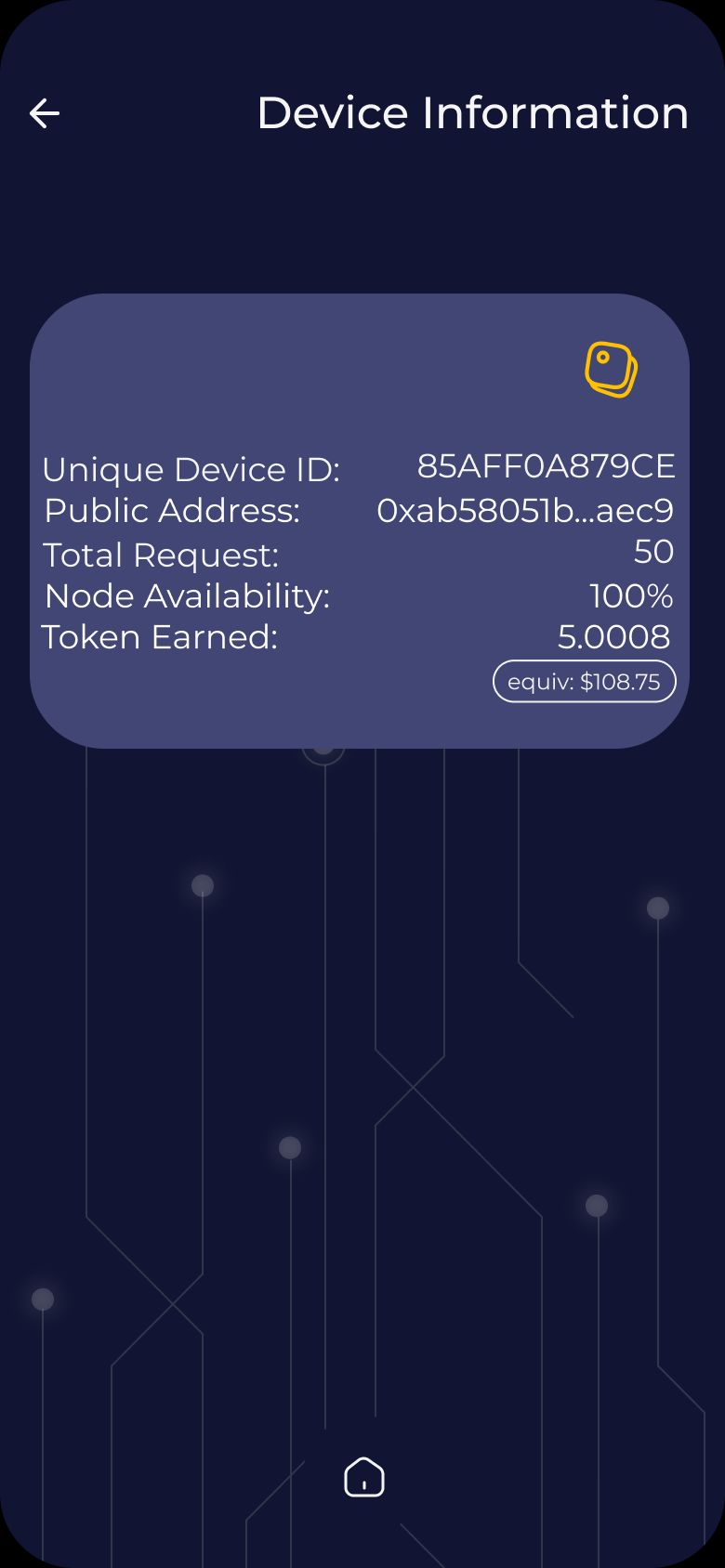
To ensure low operations and setup costs, the Oracle nodes will operate on mobile computing devices, which offer more efficient power consumption for computation while leveraging the accessibility and availability of mobile devices. There is no need for a complex setup; all that will be required is to download the node application, connect a wallet, connect the required hardware device, and stake some tokens to finalize registration. In just a few minutes, a user can set up a node that will be recognized by the entire network.
Easy integration
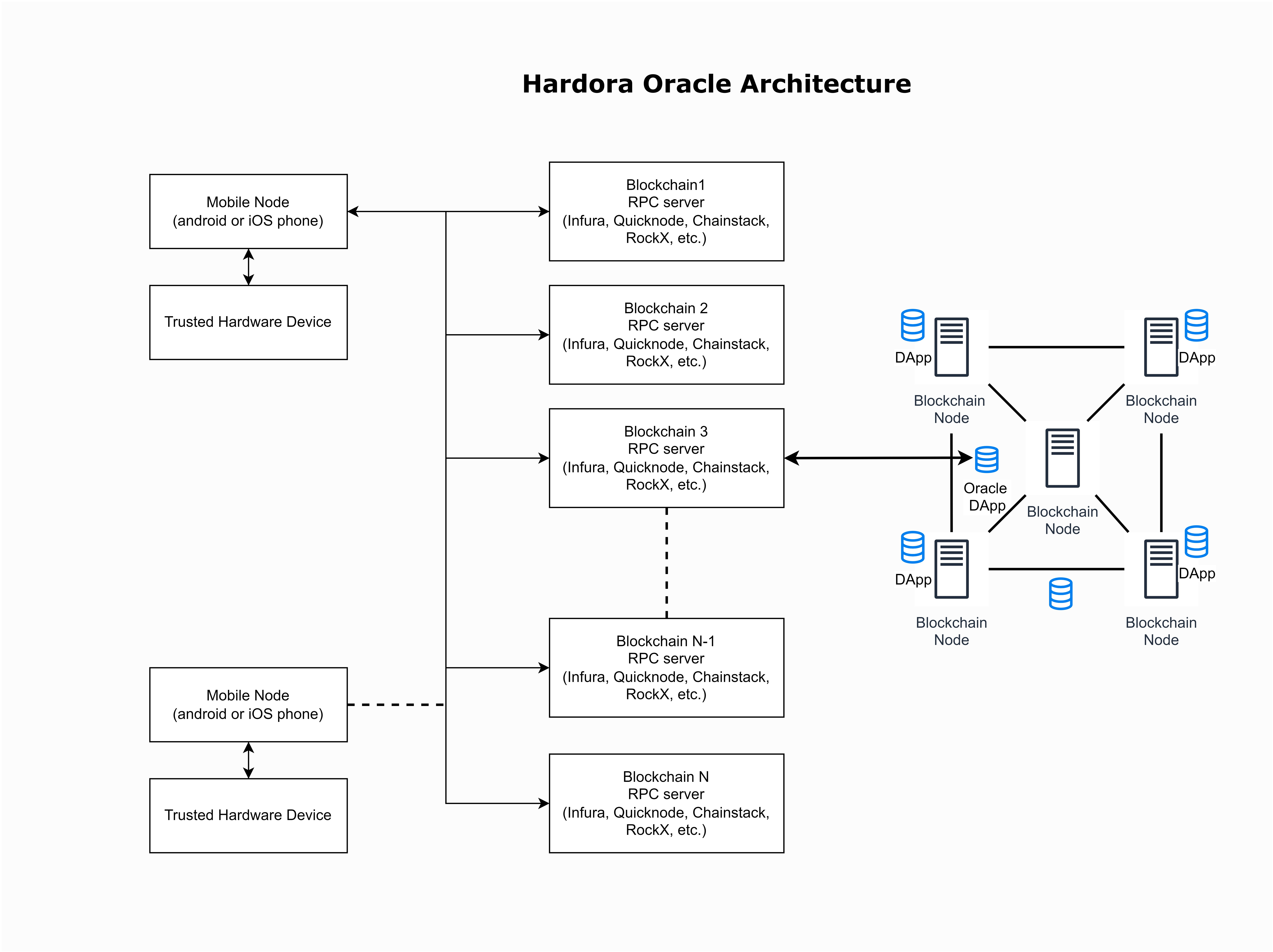
The Hardora architecture is designed to allow easy integration with any EVM-based, EVM-compatible, or any blockchain that can execute smart contracts. The Oracle Controller runs on the blockchain itself, while the nodes run off-chain on mobile devices.
Scalability
Scalability is one big issue that is addressed by our decentralized and mobile approach. The goal is to ensure that as more networks are supported, the nodes can keep generating and validating data for on-chain usage by DApps and even off-chain apps. Our modular approach, will ensure that more functionalities can be added simply by creating and deploying the smart contract for that function on all supported blockchains.
HOW IT WORKS
The main component of the Hardora oracle are:
A blockchain RPC like Infura to connect the mobile node to the blockchain nodes
A mobile device: referred to as mobile node in this context and
A hardware device (Trusted device)
The mobile node communicates with a blockchain RPC node in order to interact with the Oracle smart contracts running on the various validators/nodes of a blockchain. To create a scalable and decentralized Oracle network, the Hardora Oracle runs on mobile devices: which are known to be accessible to over 3 billion people worldwide and are connected to the internet almost all the time. This is important in countries where people don’t have access to a robust internet infrastructure to provide the accessibility required by an Oracle network.
The interaction starts when a Smart contract on blockchain-A requests data from the oracle smart contract running on the same blockchain through internal transactions. The oracle smart contract receives this data request and sends an invocation command to a selected node (an EOA) to sign and acknowledge the data request. The node app request or generates the needed data, sign it and initiate a new transaction to the smart contract that requested the data. Once the data is received by the smart contract and verified, it is sent to the smart contract that requested the data initially.
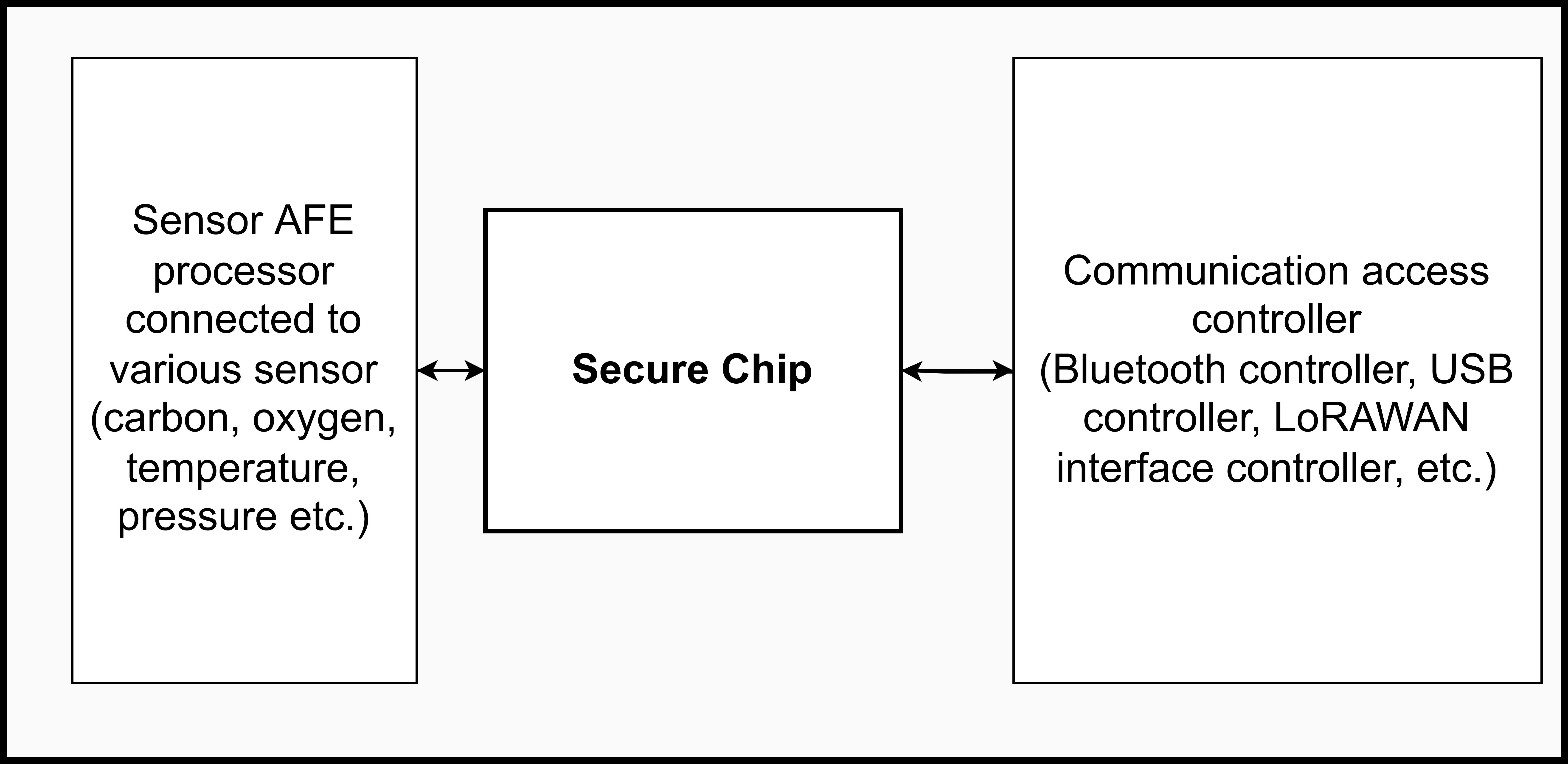
The mobile device is the physical device on which the node app runs. The node app on the device is connected to a dedicated hardware device similar to a hardware wallet, which performs non-deterministic calculations off-chain, while the node app performs deterministic computations. Deterministic data can be verified by any number of mobile nodes such as verifying user membership on a database like Polybase, while non-deterministic data cant be verified by other mobile nodes as the data produced is unique such as random numbers and thus must be generated by a trusted device.
The essence of the Hardora oracle is to provide off-chain data or computation that would have been otherwise expensive to execute or impossible to access by DApps running on blockchain nodes. Combining a mobile device and a dedicated hardware device ensures we can serve quality data that is either deterministic or not, based on the demand of the DApps requesting those data.
Possible data services provided by the protocol include:
Generating random numbers
Computing the hash of a file
Verifying data stored in a decentralized database like Polybase
Retrieving location-specific carbon data
Retrieving location-specific temperature data
File hash computations and many more.
How it's Made
THE MOBILE APP
Figma was used to design the mobile mockup which was used in developing the The node app was developed using ReactNative. Web3.js library was used for interacting with the Oracle Smart contract
THE ORACLE SMART CONTRACT
Using REMIX IDE the oracle contract was written in solidity and was deployed on several EVM-compatible L1 and L2 blockchains.
The DEMO app smart contract
The oracle contract was written in solidity and was deployed on several EVM-compatible L1 and L2 blockchains